HTTPS 工作原理
理解 HTTP 协议,对称和非对称加密,了解 HTTPS 协议的工作原理
注:本文系全文转载,原文信息如下:
作者:猫尾博客
链接:https://cattail.me/tech/2015/11/30/how-https-works.html
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
读完本文,你能明白
- 什么是 HTTPS,TLS(SSL),TLS 和 HTTPS 是什么关系
- 什么是证书和数字签名,它们是如何传递信任的
- HTTPS 有什么样的功能,它是如何实现这样的功能的
HTTPS 工作原理简介
HTTPS,也称作 HTTP over TLS。TLS 的前身是 SSL,TLS 1.0 通常被标示为 SSL 3.1,TLS 1.1 为 SSL 3.2,TLS 1.2 为 SSL 3.3。本文着重描述 TLS 协议的 1.2 版本。
下图描述了在 TCP/IP 协议栈中 TLS(各子协议)和 HTTP 的关系:
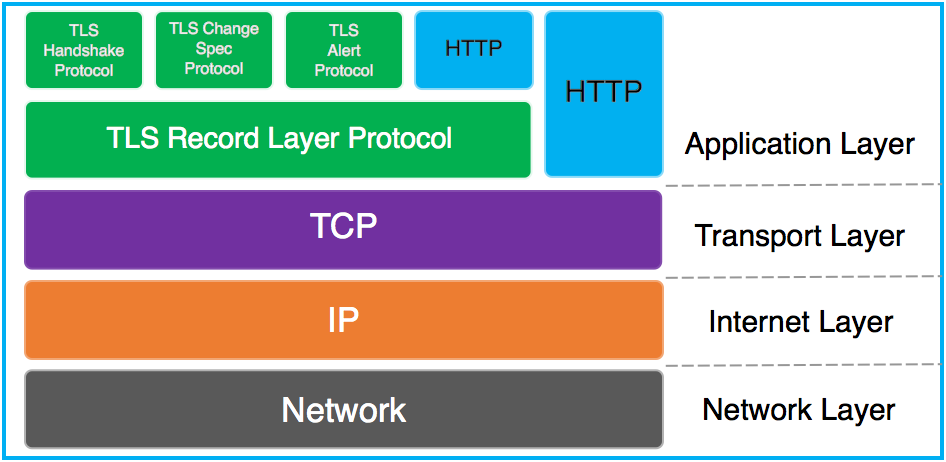
其中 Handshake Protocol、Change Ciper Spec Protocol 和 Alert Protocol 组成了 SSL Handshaking Protocols。
HTTPS 和 HTTP 协议相比提供了:
- 数据完整性:内容传输经过完整性校验
- 数据隐私性:内容经过对称加密,每个连接生成一个唯一的加密密钥
- 身份认证:第三方无法伪造服务端(客户端)身份
其中,数据完整性和隐私性由 TLS Record Protocol 保证,身份认证由 TLS Handshaking Protocols 实现。
总览
使用 RSA 算法的 SSL 握手过程是这样的:
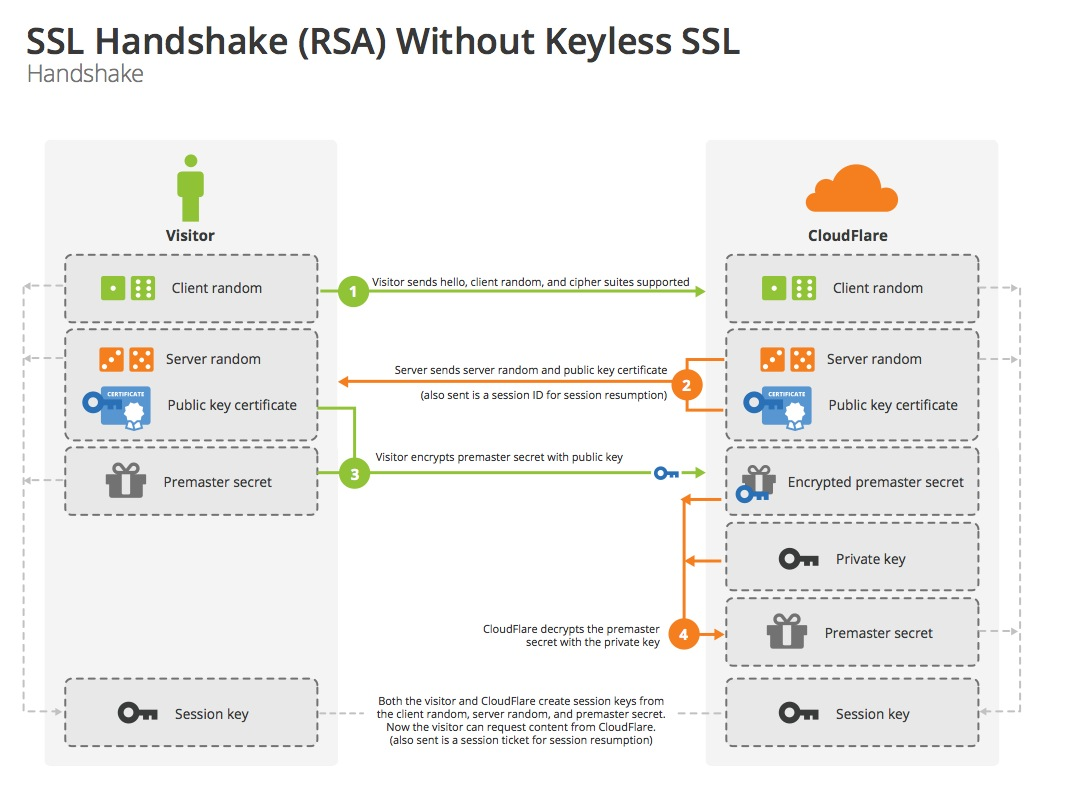
- [明文]客户端发送随机数 client_random 和支持的加密方式列表
- [明文]服务器返回随机数 server_random,选择的加密方式和服务器证书链
- [RSA]客户端验证服务器证书,使用证书中的公钥加密 premastersecret 发送给服务端
- 服务端使用私钥解密 premastersecret
- 两端分别通过 client_random,server_random 和 premastersecret 生成 mastersecret,用于对称加密后续通信内容
证书(Digital Certificate)
那么什么是证书呢?
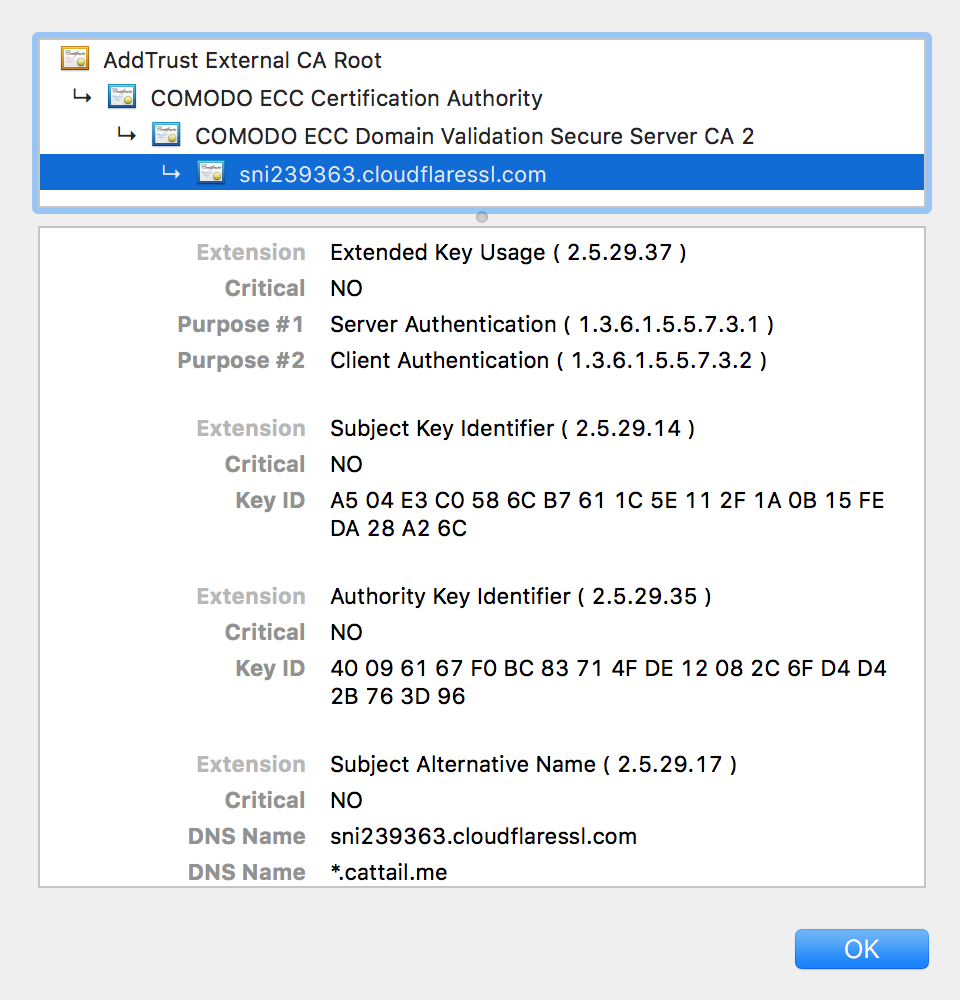
证书中包含了以下信息
- 证书信息:过期时间和序列号
- 所有者信息:姓名等
- 所有者公钥
为什么服务端要发送证书给客户端?
互联网有太多的服务需要使用证书来验证身份,以至于客户端(操作系统或浏览器等)无法内置所有证书,需要通过服务端将证书发送给客户端。
客户端为什么要验证接收到的证书
中间人攻击
客户端 <------------ 攻击者 <------------ 服务端
伪造证书 拦截请求客户端如何验证接收到的证书
为了回答这个问题,需要引入数字签名 (Digital Signature)。
+---------------------+
| A digital signature |
|(not to be confused |
|with a digital |
|certificate) | +---------+ +--------+
| is a mathematical |---- 哈希 --->| 消息摘要 |--- 私钥加密 --->| 数字签名 |
|technique used | +---------+ +--------+
|to validate the |
|authenticity and |
|integrity of a |
|message, software |
|or digital document. |
+---------------------+将一段文本通过哈希(hash)和私钥加密处理后生成数字签名。
假设消息传递在 Bob,Susan 和 Pat 三人之间发生。Susan 将消息连同数字签名一起发送给 Bob,Bob 接收到消息后,可以这样验证接收到的消息就是 Susan 发送的
+---------------------+
| A digital signature |
|(not to be confused |
|with a digital |
|certificate) | +---------+
| is a mathematical |---- 哈希 --->| 消息摘要 |
|technique used | +---------+
|to validate the | |
|authenticity and | |
|integrity of a | |
|message, software | 对
|or digital document. | 比
+---------------------+ |
|
|
+---------+ +----------+
| 数字签名 |--- 公钥解密 --->| 消息摘要 |
+---------+ +----------+当然,这个前提是 Bob 知道 Susan 的公钥。更重要的是,和消息本身一样,公钥不能在不安全的网络中直接发送给 Bob。
此时就引入了证书颁发机构(Certificate Authority,简称 CA),CA 数量并不多,Bob 客户端内置了所有受信任 CA 的证书。CA 对 Susan 的公钥(和其他信息)数字签名后生成证书。
Susan 将证书发送给 Bob 后,Bob 通过 CA 证书的公钥验证证书签名。
Bob 信任 CA,CA 信任 Susan 使得 Bob 信任 Susan,信任链(Chain Of Trust)就是这样形成的。
事实上,Bob 客户端内置的是 CA 的根证书 (Root Certificate),HTTPS 协议中服务器会发送证书链(Certificate Chain)给客户端。
TLS 协议
TLS协议包括TLS Record Protocol和TLS Handshake Protocol。总览中的流程图仅涉及到TLS Handshake Protocol。
TLS Record Protocol
在TLS协议中,有四种子协议运行于Record Protocol之上
- Handshake protocol
- Alert protocol
- Change cipher spec protocol
- Application data protocol
Record protocol 起到了这样的作用
- 在发送端:将数据(Record)分段,压缩,增加 MAC(Message Authentication Code)和加密
- 在接收端:将数据(Record)解密,验证 MAC,解压并重组
值得一提的是,Record protocol 提供了数据完整性和隐私性保证,但 Record 类型(type)和长度(length)是公开传输的
Record Protocol 有三个连接状态(Connection State),连接状态定义了压缩,加密和 MAC 算法。所有的 Record 都是被当前状态(Current State)确定的算法处理的。
TLS Handshake Protocol和Change Cipher Spec Protocol会导致Record Protocol状态切换。
empty state -------------------> pending state ------------------> current state
Handshake Protocol Change Cipher Spec初始当前状态(Current State)没有指定加密,压缩和 MAC 算法,因而在完成 TLS Handshaking Protocols 一系列动作之前,客户端和服务端的数据都是明文传输的;当 TLS 完成握手过程后,客户端和服务端确定了加密,压缩和 MAC 算法及其参数,数据(Record)会通过指定算法处理。
其中,Record 首先被加密,然后添加 MAC(message authentication code)以保证数据完整性。
TLS Handshake Protocol
Handshakeing protocols 包括 Alert Protocol,Change Cipher Spec Protocol 和 Handshake protocol。本文不会详细介绍 Alert Protocol 和 Change Cipher Spec Protocol。
使用RSA算法的握手过程是这样的(已在总览中提到)

客户端和服务端在握手 hello 消息中明文交换了client_random和server_random,使用RSA公钥加密传输premastersecret,最后通过算法,客户端和服务端分别计算mastersecret。其中,不直接使用premastersecret的原因是:保证secret的随机性不受任意一方的影响。
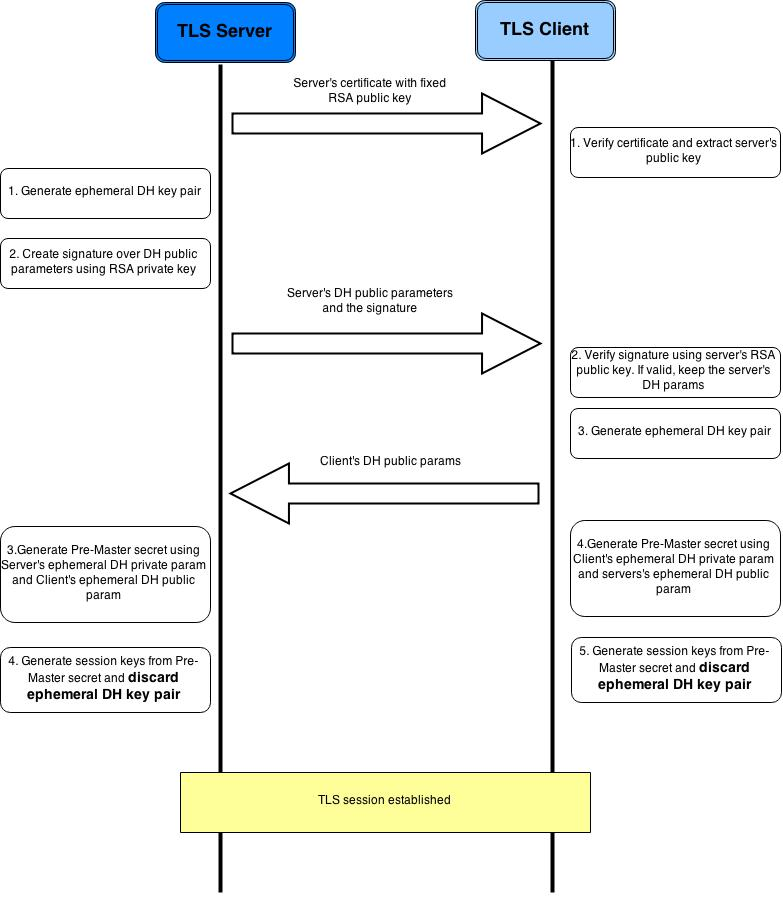
除了使用RSA算法在公共信道交换密钥,还可以通过Diffie–Hellman算法。Diffie–Hellman算法的原理是这样的
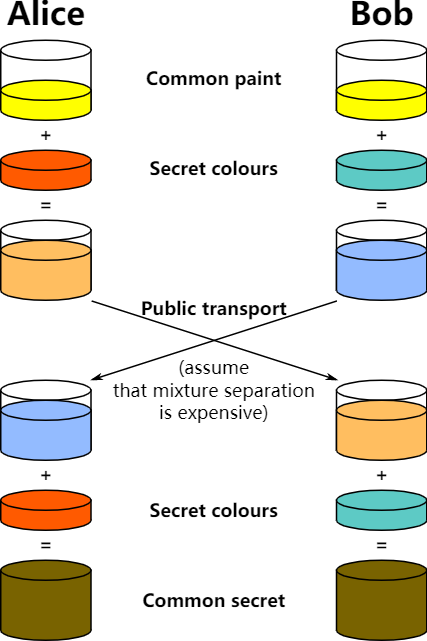
使用Diffie–Hellman算法交换premastersecret的流程

小结
TLS Handshake Protocol协商了TLS Record Protocol使用的算法和所需参数,并验证了服务端身份;
TLS Record Protocol在协商后保证应用层数据的完整性和隐私性。
TLS Handshake Protocol的核心是在公开信道上传递premastersecret。
Q&A
为什么传输内容不直接使用非对称加密?
因为性能限制。
HTTPS 能保证正常连接?
不能。
攻击者甚至可以直接丢弃双方的数据包
服务端如何验证客户端身份?
通过Client Certificate
Alert protocol 有什么作用?
Closure Alerts:防止Truncation Attack
Error Alerts:错误处理
master secret 是如何计算的
master_secret = PRF (pre_master_secret, "master secret",
ClientHello.random + ServerHello.random)
[0..47];加密,压缩和 MAC 算法参数是如何计算的
Handshaking Protocols使得客户端和服务端交换了三个参数:client_random,server_random和master_secret,通过以下算法生成算法所需要的参数
To generate the key material, compute
key_block = PRF (SecurityParameters.master_secret,
"key expansion",
SecurityParameters.`server_random` +
SecurityParameters.`client_random`);
until enough output has been generated. Then, the key_block is
partitioned as follows:
client_write_MAC_key [SecurityParameters.mac_key_length]
server_write_MAC_key [SecurityParameters.mac_key_length]
client_write_key [SecurityParameters.enc_key_length]
server_write_key [SecurityParameters.enc_key_length]
client_write_IV [SecurityParameters.fixed_iv_length]
server_write_IV [SecurityParameters.fixed_iv_length]使用Diffie-Hellman算法的TLS握手细节
拓展阅读
- Keyless
- Let’s Encrypt
- Session resume
- 证书 Revoke
参考
-
[1] TLS1.2 规范
-
[2] PKI 规范
-
[3] 证书和数字签名
-
[4] TLS Handshake